Earthworms could help reduce antibiotic resistance genes in soil - American Chemical Society
$ 16.50 · 4.7 (627) · In stock


The role of earthworms in agronomy: Consensus, novel insights and remaining challenges - ScienceDirect
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text

Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Agroecosystems as Emerging Contaminants

Earthworm activity optimized the rhizosphere bacterial community structure and further alleviated the yield loss in continuous cropping lily (Lilium lancifolium Thunb.)
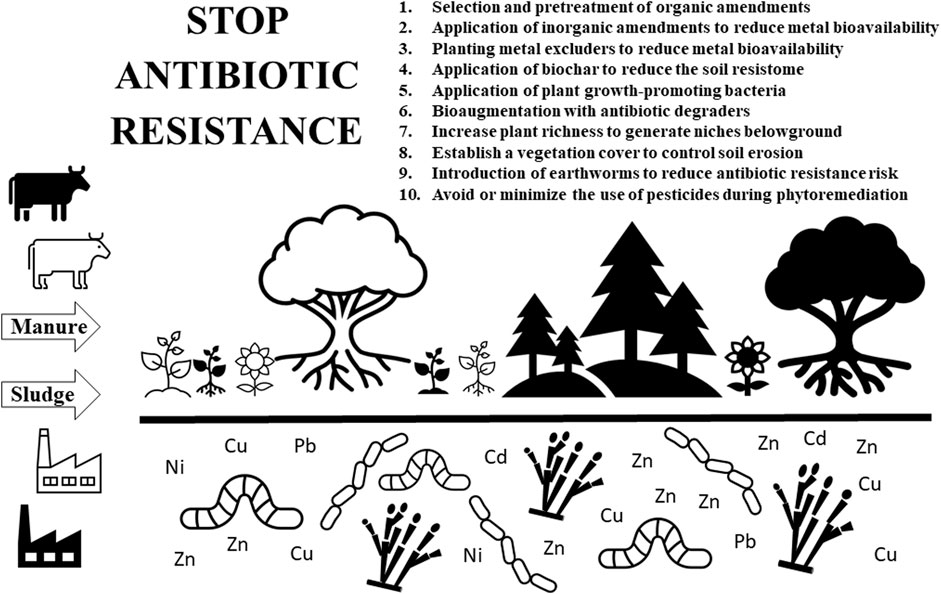
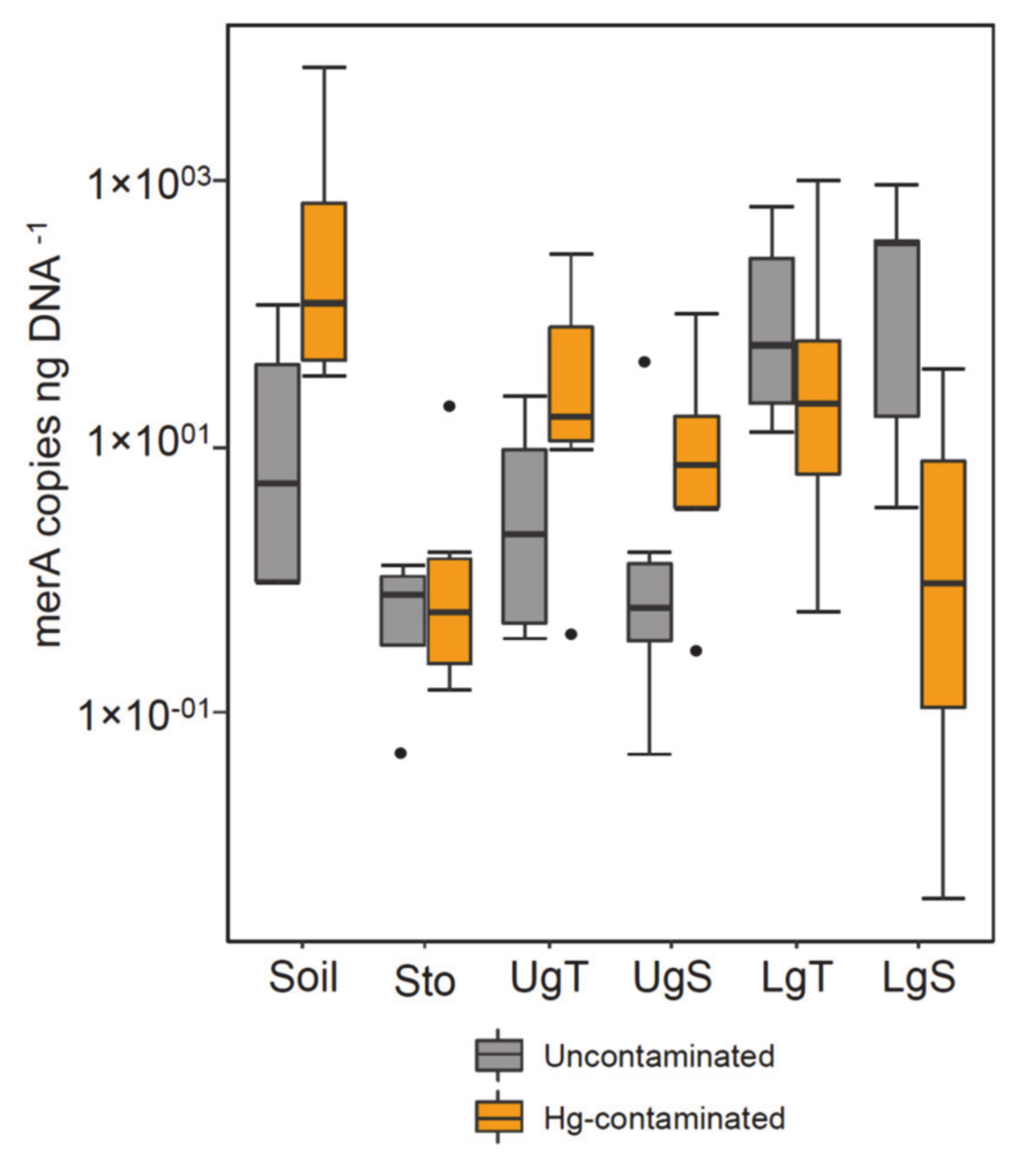
Frontiers Enhanced phytoremediation of metal contaminated soils aimed at decreasing the risk of antibiotic resistance dissemination

The role of earthworms in agronomy: Consensus, novel insights and remaining challenges - ScienceDirect

Insights into the mechanisms underlying the remediation potential of earthworms in contaminated soil: A critical review of research progress and prospects - ScienceDirect
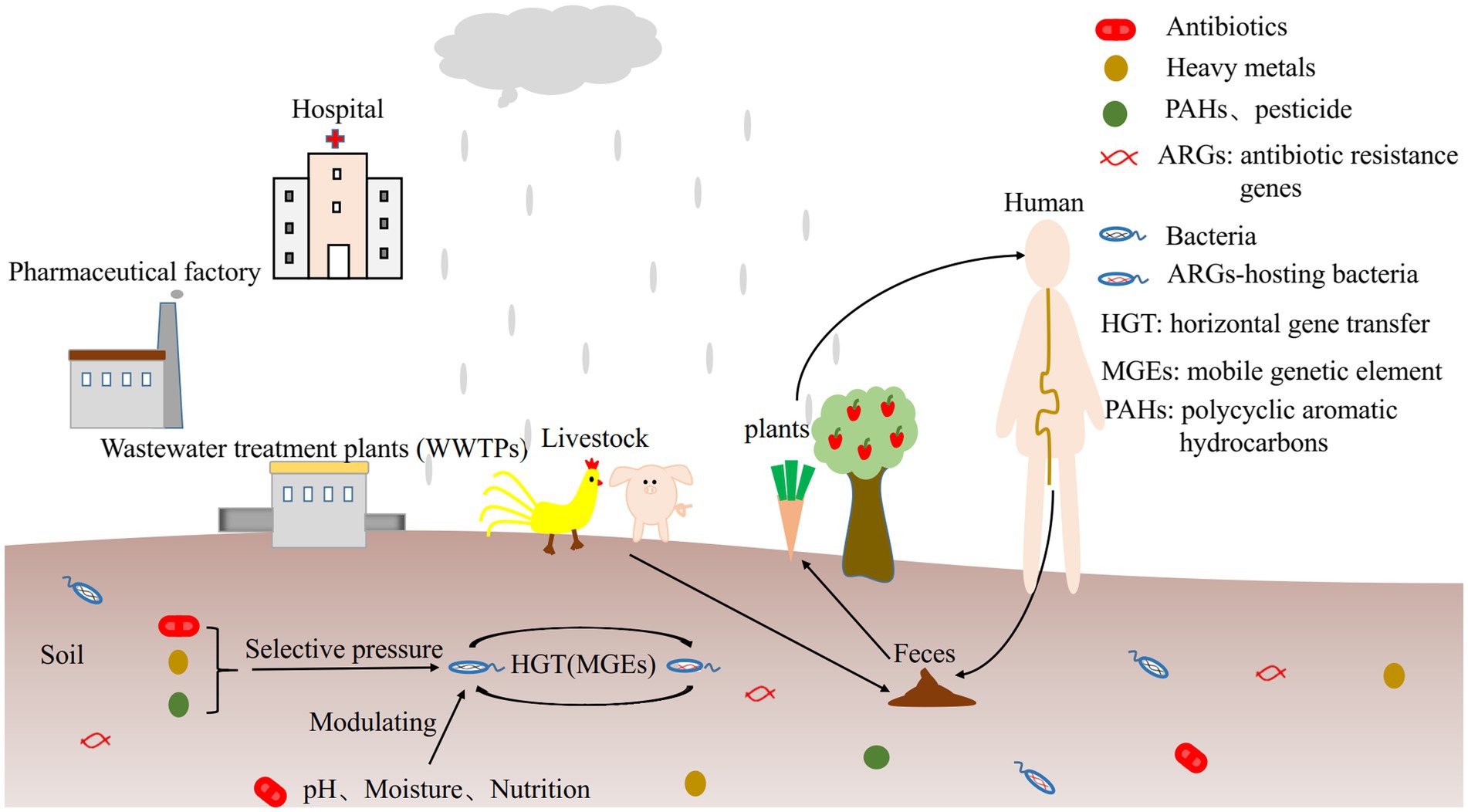
Frontiers The source, fate and prospect of antibiotic resistance genes in soil: A review

Earthworms a Natural and Sustainable Solution for Reducing Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Soil

Factors affecting population dynamics of earthworm.

Removal of sulfamethoxazole and antibiotic resistance genes in paddy soil by earthworms (Pheretima guillelmi): Intestinal detoxification and stimulation of indigenous soil bacteria - ScienceDirect